뇌졸중 후 자연회복된 마우스에서 RNA-시퀀싱 분석을 통한 운동대뇌피질 변이체의 확인
배경 및 목적 - 많은 수복 치료법이 뇌졸중 후 뇌 손상을 연구하는데 사용되고 있으며, 이러한 치료에 의해 유도된 변화는 뇌 회복 및 회복 기전에 대한 중요한 이해를 제공하였다. 그러나 본질적인 뇌졸중 후 자연 회복에서 일어나는 변화는 다소 불분명하다. 본 연구의 목적은 뇌졸중 후 자연 회복 된 마우스의 일차 운동 피질의 전사체를 직접 조사함으로써 뇌졸중 후 자연 회복의 본질적인 변화를 밝히는데 있다.
방법 - 수컷 C57BL / 6J 마우스에 중대뇌동맥 폐색을 통한 일과성 국소 허혈 모델을 제작하였으며, 기능 회복 평가는 수평 회전 빔 시험을 수행하였다. 경색 크기와 위치를 평가하기 위해 새로운 심층 병변 매핑 분석이 사용되었으며, 손상측 및 손상 반대측 일차 운동피질 (iM1 및 cM1)에서 RNA-시퀀싱 전사체 분석을 수행하였다.
결과 - 뇌졸중 마우스의 행동 수행에 대한 클러스터 분석 결과 복구되지 않은 그룹과 자발적으로 회복된 그룹, 2가지로 구분되어 나타났으며, 이러한 두 군간의 회복차이에도 불구하고 두 군 모두 유사한 병변 프로파일을 보인 반면, RNA-시퀀싱 전사체 분석결과 자발적으로 회복된 뇌졸중 마우스의 iM1과 cM1 모두에서 구별되는 생물학적 경로를 나타내었다. 상관 관계 분석 결과, iM1에서는 유전자 38 개가 개선된 회복에 유의한 상관 관계가 있었으며, cM1에서는 74 개의 유전자가 상관 관계가 있었다. 오믹스데이터 분석을 통해 패스웨이와 네트워크등을 나타내기 위한 ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA)를 수행한 결과, cM1에서 cAMP 신호 전달과 관련성이 높았으며, Adora2a (아데노신 수용체 A2A), Drd2 (도파민 수용체 D2) 및 Pde10a (포스포디에스테라제 10A) 발현의 선택적인 감소가 나타났다. 특히, cM1에서 이들 유전자의 발현은 행동 회복과 부정적 상관 관계가 있었다.
결론 – 본 연구의 RNA-시퀀싱 결과는 자발적으로 회복된 뇌졸중 마우스의 운동피질에서 회복 관련 유전자를 밝혀 내었으며 뇌졸중 후 자발회복에 손상 반대편 대뇌피질에서의 Adora2a, Drd2 및 Pde10a가 매개하는 cAMP 신호 전달 경로가 관련되는 것을 강조하였다. 뇌졸중 후 이들 후보자를 표적으로하는 약물 개발은 유익한 회복 결과를 제공 할 수 있을것이다.
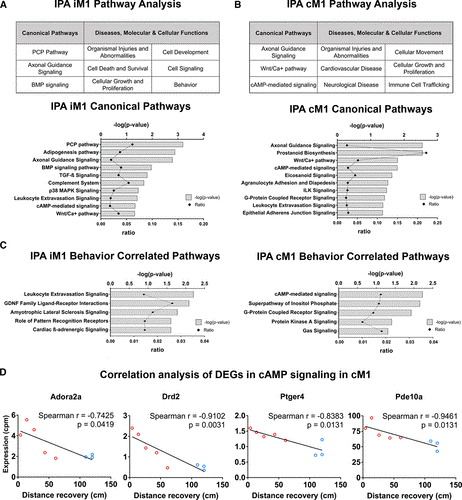
Figure 5. Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) of RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) transcriptome highlights the involvement of cAMP-mediated signaling in the contralesional primary motor cortex (cM1). A–B, IPA of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the (A) ipsilesional primary motor cortex (iM1) or (B) cM1 (upper tables) in recovered stroke mice indicated significant top canonical pathways and diseases, molecular/cellular functions. Bar graphs indicated significant top canonical pathways in (A) iM1 and (B) cM1 (lower graphs), plotted by P values (Fisher exact test) and ratio (number of genes in pathway). C, Bar graphs demonstrate significant top 5 relevant canonical pathways correlated with recovery in the iM1 (left) and cM1 (right). D, Scatter plots demonstrated significant negative correlations (Spearman) between gene expression levels (RNA-seq counts per million based) of 4 DEGs in cAMP-mediated signaling in the cM1 (Adora2a [adenosine receptor A2A], Drd2 [dopamine receptor D2], Ptger4 [prostaglandin E receptor 4], and Pde10a [phosphodiesterase 10A]) and the behavior recovery outcome (rotating beam distance at poststroke day 14). Each line depicted linear regression for each scatter plot (n=3 recovered, n=5 nonrecovered mice). BMP indicates bone morphogenetic protein; and PCP, planar cell polarity.
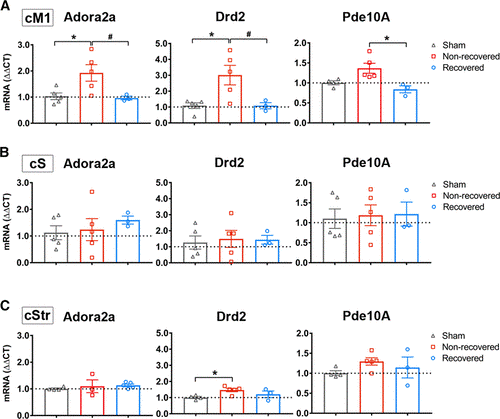
Figure 6. Adora2a (adenosine receptor A2A), Drd2 (dopamine receptor D2), and Pde10a (phosphodiesterase 10A) were selectively decreased in contralesional primary motor cortex (cM1) of recovered mice. A–B, Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) verification of Adora2a (A), Drd2 (B), and Pde10a (C) mRNA expression in recovered and nonrecovered stroke mice and nonstroke sham mice in each region: cM1 (upper), contralesional somatosensory cortex (cS; middle), and contralesional somatosensory striatum (cStr; lower). Graphs indicated gene expression levels relative to sham group. GAPDH was used as reference gene. Data were expressed as mean ΔΔCT±SEM. The dotted horizontal line indicates ΔΔCT=1.0. *P<0.05 1-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni test indicates a significant difference from sham (n=5), and #P<0.05 indicates a significant difference between recovered (n=3) and nonrecovered group (n=5).
RNA-Sequencing Analysis Revealed a Distinct Motor Cortex Transcriptome in Spontaneously Recovered Mice After Stroke. Masaki Ito, Markus Aswendt, Alex G. Lee, Shunsuke Ishizaka, Zhijuan Cao, Eric H. Wang, Sabrina L. Levy, Daniel L. Smerin, Jennifer A. McNab, Michael Zeineh, Christoph Leuze, Maged Goubran, Michelle Y. Cheng, and Gary K. Steinberg. Stroke. 2018; 49:2191–2199.
|